Storage Events
When dealing with storage operations, it's important to note that document changes can impact the entire application. That's why we provide the ability to manage storage events, enabling you to trigger events when documents are created, updated, or removed within your storage system.
Supported Event types
At present, we offer support for the following storage events:
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
on_created |
This event is triggered when a new document is created within the specified storage. |
on_saved |
This event is triggered when a new document is created or an existing document is updated within the specified storage. |
on_updated |
This event is triggered when an existing document is updated within the specified storage. |
on_removed |
This event is triggered when an existing document is marked as removed within the specified storage. |
Event Execution
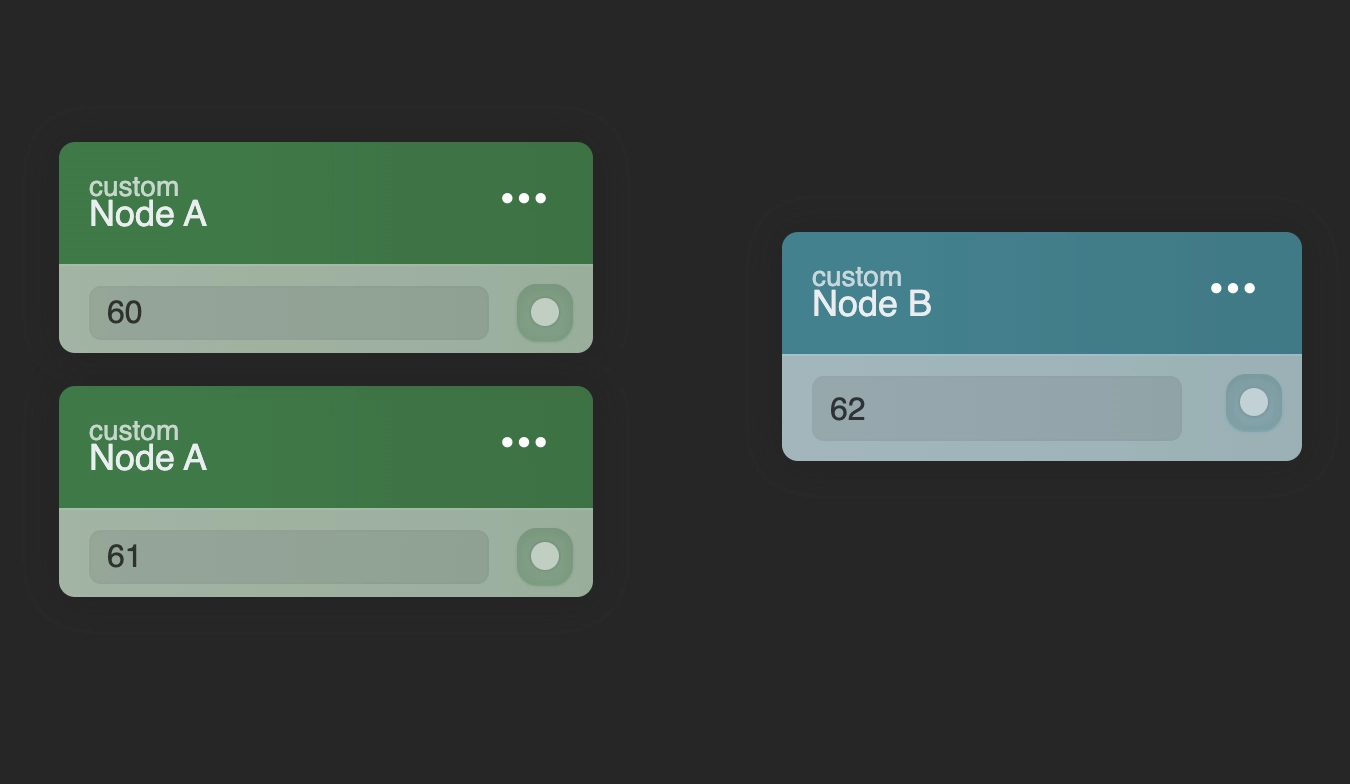
Storage Events operate on a First In, First Out (FIFO) basis, although simultaneous execution by multiple nodes is possible. For instance, while Node A is processing Event 61, Node B might already be executing Event 62, due to Node A concurrently processing Event 60, which Node B is not. Given the variability in processing speeds across different nodes, the FIFO execution logic for these events cannot be guaranteed.
Within the blueprint function, you can manage the execution order using lock & wait blocks. However, this approach may decelerate other events that are executing in the same thread and block. To ensure a 100% guarantee of execution order, it is advisable to offload the intensive tasks of Storage Events and transfer them to a queue.
Event Payload
When a document is created or updated, we will furnish you with the most recent document data, along with a list of fields that have undergone modifications. The document you receive represents the current state of the document at the moment of the event.
Given the extremely rapid and high-performance nature of these events, they may occasionally be combined. To provide you with a clearer understanding of what might occur in such rare scenarios, we've included a JSON example below illustrating the functioning of Storage Events.
Document Created Flow
Document Updated Flow
Document Fast Updated Flow
It's worth noting that when updates occur at high speed, the triggered events may be consolidated. Below is an example of such a combined event. If a key has been modified multiple times, it will appear multiple times in the revisions array.